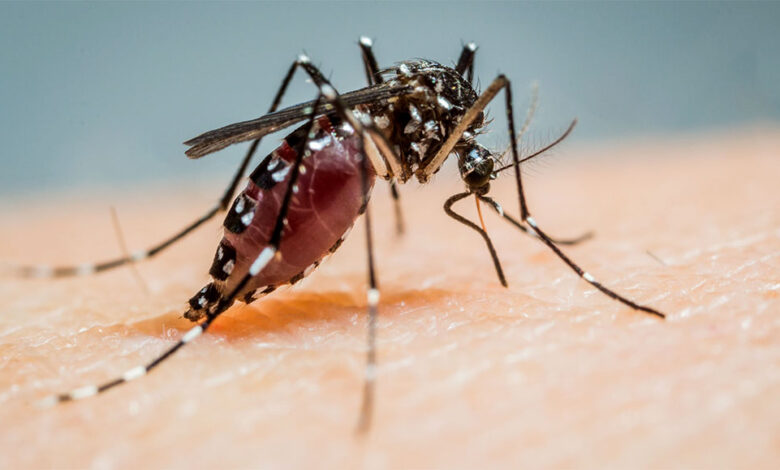
Mosquitoes taste you before they decide to bite

amino acids: Simple molecules that occur naturally in plant and animal tissues and that are the basic building blocks of proteins.
behavior: The way something, often a person or other organism, acts towards others, or conducts itself.
biologist: A scientist involved in the study of living things.
cell: (in biology) The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Typically too small to see with the unaided eye, it consists of a watery fluid surrounded by a membrane or wall. Depending on their size, animals are made of anywhere from thousands to trillions of cells..
chemical: A substance formed from two or more atoms that unite (bond) in a fixed proportion and structure. For example, water is a chemical made when two hydrogen atoms bond to one oxygen atom.
climate change: Long-term, significant change in the climate of Earth. It can happen naturally or in response to human activities, including the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests.
compound: (often used as a synonym for chemical) A compound is a substance formed when two or more chemical elements unite (bond) in fixed proportions. For example, water is a compound made of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.
dengue: A potentially lethal infectious disease transmitted by mosquitoes. No vaccine yet exists to prevent infection with the virus responsible for the disease, which causes high fevers, severe headache, joint pain, pain behind the eyes, rash, bone pain and sometimes mild bleeding.
factor: Something that plays a role in a particular condition or event; a contributor.
genetic: Having to do with chromosomes, DNA and the genes contained within DNA. The field of science dealing with these biological instructions is known as genetics. People who work in this field are geneticists.
insect: A type of arthropod that as an adult will have six segmented legs and three body parts: a head, thorax and abdomen. There are hundreds of thousands of insects, which include bees, beetles, flies and moths.
insight: The ability to gain an accurate and deep understanding of a situation just by thinking about it, instead of working out a solution through experimentation.
labella: (sing. labellum) The central — and usually lower — petal of an orchid bloom. It’s often bigger than other petals, with a different shape. It’s also the term for the paired lobes found in some insects at the tip of their proboscis.
malaria: A disease caused by a parasite that invades the red blood cells. The parasite is transmitted by mosquitoes, largely in tropical and subtropical regions.
microbe: Short for microorganism. A living thing that is too small to see with the unaided eye, including bacteria, some fungi and many other organisms such as amoebas. Most consist of a single cell.
microscope: An instrument used to view objects, like bacteria, or the single cells of plants or animals, that are too small to be visible to the unaided eye.
molecule: An electrically neutral group of atoms that represents the smallest possible amount of a chemical compound. Molecules can be made of single types of atoms or of different types. For example, the oxygen in the air is made of two oxygen atoms (O2), but water is made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (H2O).
proboscis: A straw-like mouthpiece in bees, moths and butterflies used for sucking up liquids. The term can also be applied to an animal’s long snout (such as in an elephant).
protein: A compound made from one or more long chains of amino acids. Proteins are an essential part of all living organisms. They form the basis of living cells, muscle and tissues; they also do the work inside of cells. Antibodies, hemoglobin and enzymes are all examples of proteins. Medicines frequently work by latching onto proteins.
range: The full extent or distribution of something. For instance, a plant or animal’s range is the area over which it naturally exists. (in math or for measurements) The extent to which values can vary (such as the highest to lowest temperatures). Also, the distance within which something can be reached or perceived.
salt: A compound made by combining an acid with a base (in a reaction that also creates water). The ocean contains many different salts — collectively called “sea salt.” Common table salt is a made of sodium and chlorine.
system: A network of parts that together work to achieve some function. For instance, the blood, vessels and heart are primary components of the human body’s circulatory system. System can even be applied to the processes or ideas that are part of some method or ordered set of procedures for getting a task done.
taste: One of the basic properties the body uses to sense its environment, especially foods, using receptors (taste buds) on the tongue (and some other organs).
yellow fever: A disease that creates flu-like symptoms that can start with fever, chills, headache, backache and vomiting. Roughly 15 percent of patients may go on to develop more serious disease. This can lead to uncontrolled bleeding, the failure of multiple internal organs — and death.



